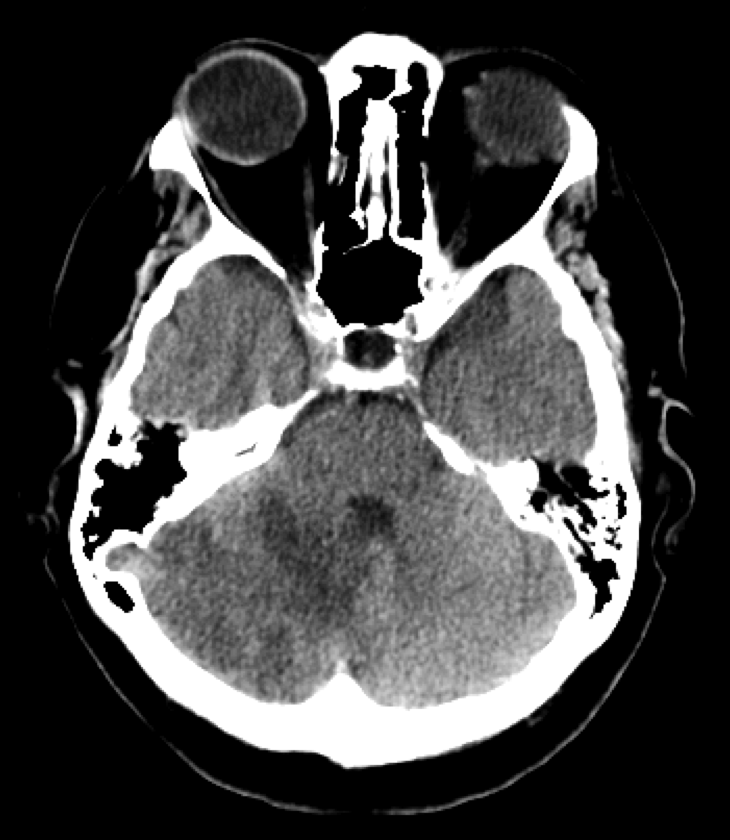
Axial CT head shows right cerebellar hypoattenuation.
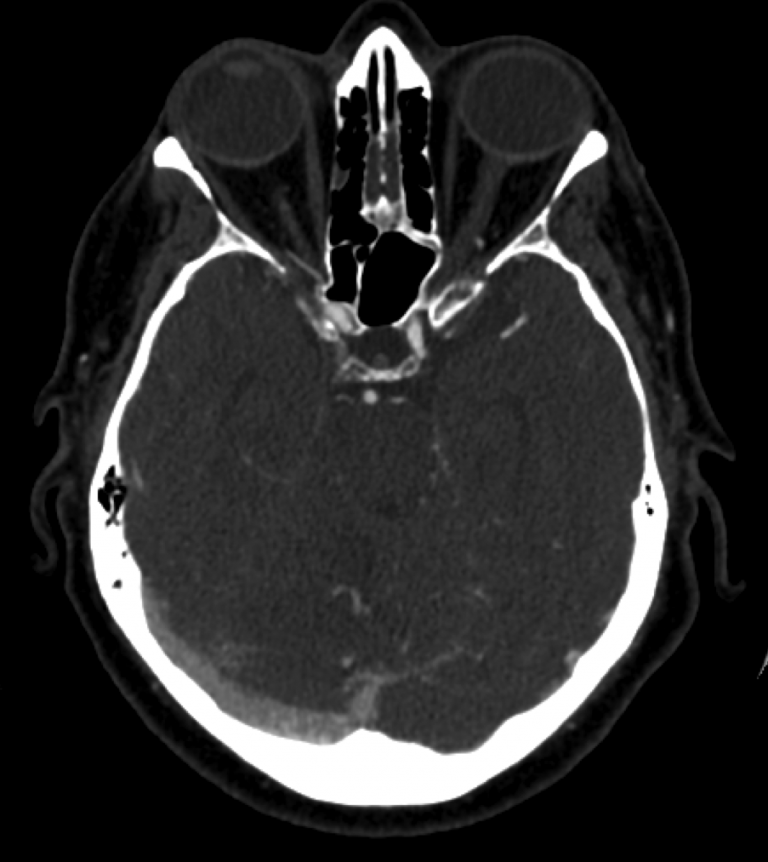
Axial CTA shows predominance of venous outflow through the right transverse sinus and minimal if any filling of the left transverse sinus.
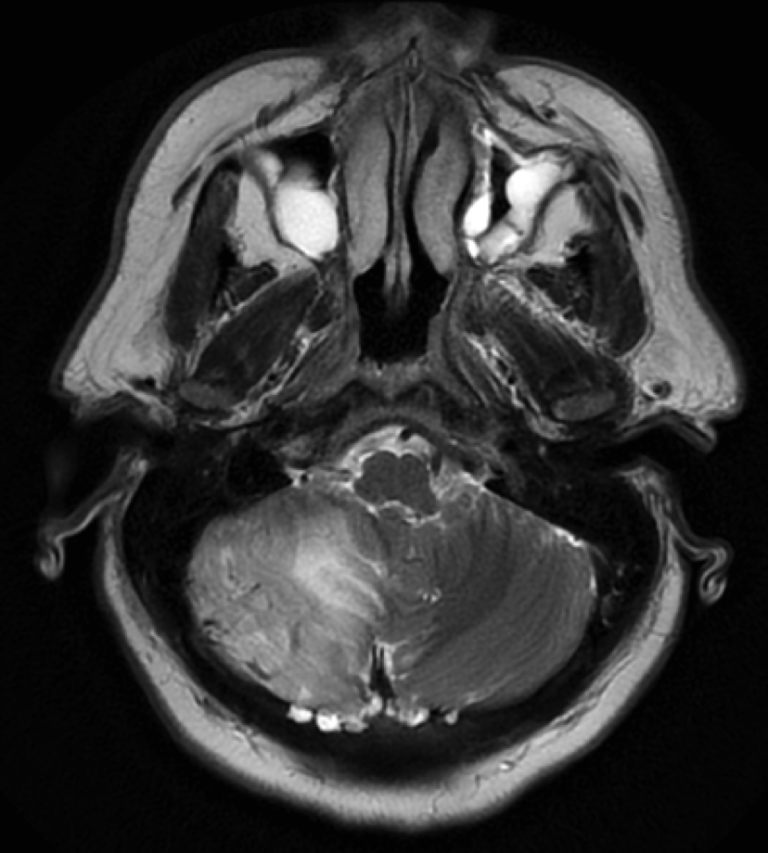
Axial T2 MR brain shows right cerebellar hyperintensity, indicating venous congestion. Prominent right cerebellar serpiginous flow voids indicate dilated veins.
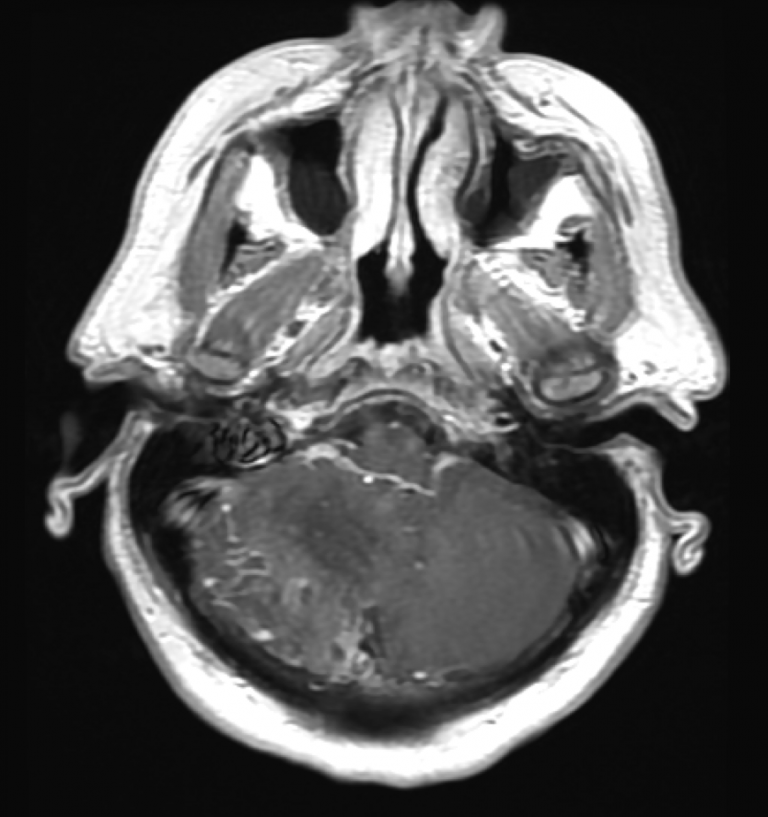
Axial T1+C MR brain shows right cerebellar focal enhancement, indicating chronic venous congestion.
Lateral projection of left external carotid artery shows a distal middle meningeal artery that supplies a dural arteriovenous fistula of the tentorium with rapid cortical venous reflux toward the cerebellum.
Lateral projection of left external carotid artery injection with focus on middle meningeal artery redemonstrates supply to the tentorial dural arteriovenous fistula with rapid cortical venous reflux toward the cerebellum.
Lateral projection of a left vertebral artery injection shows a robust posterior meningeal artery that supplies a dural arteriovenous fistula of the tentorium with rapid cortical venous reflux toward the cerebellum.







