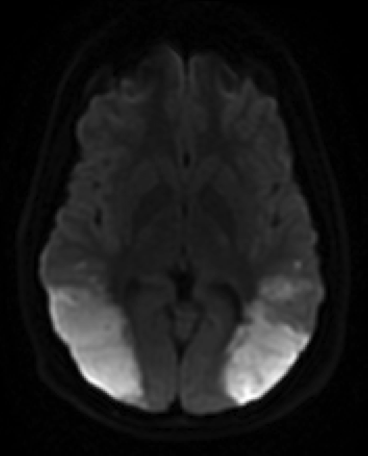
DWI sequences show large regions of restricted diffusion in the bilateral posterior temporo-parietal lobes and also in the left frontal lobe, consistent with ischemic strokes
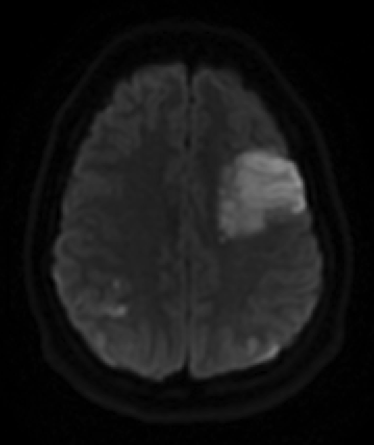
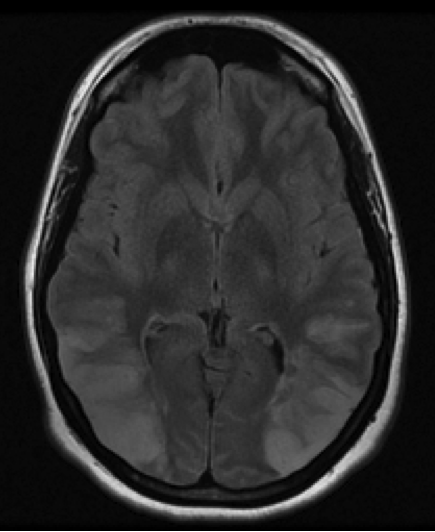
T2 FLAIR sequences show edema in these same territories.
Note the diffuse vascular “beading,” or segmental stenosis and dilation of vessels that effects the entire intracranial circulation.





